Maidenhair Tree
Ginkgo biloba
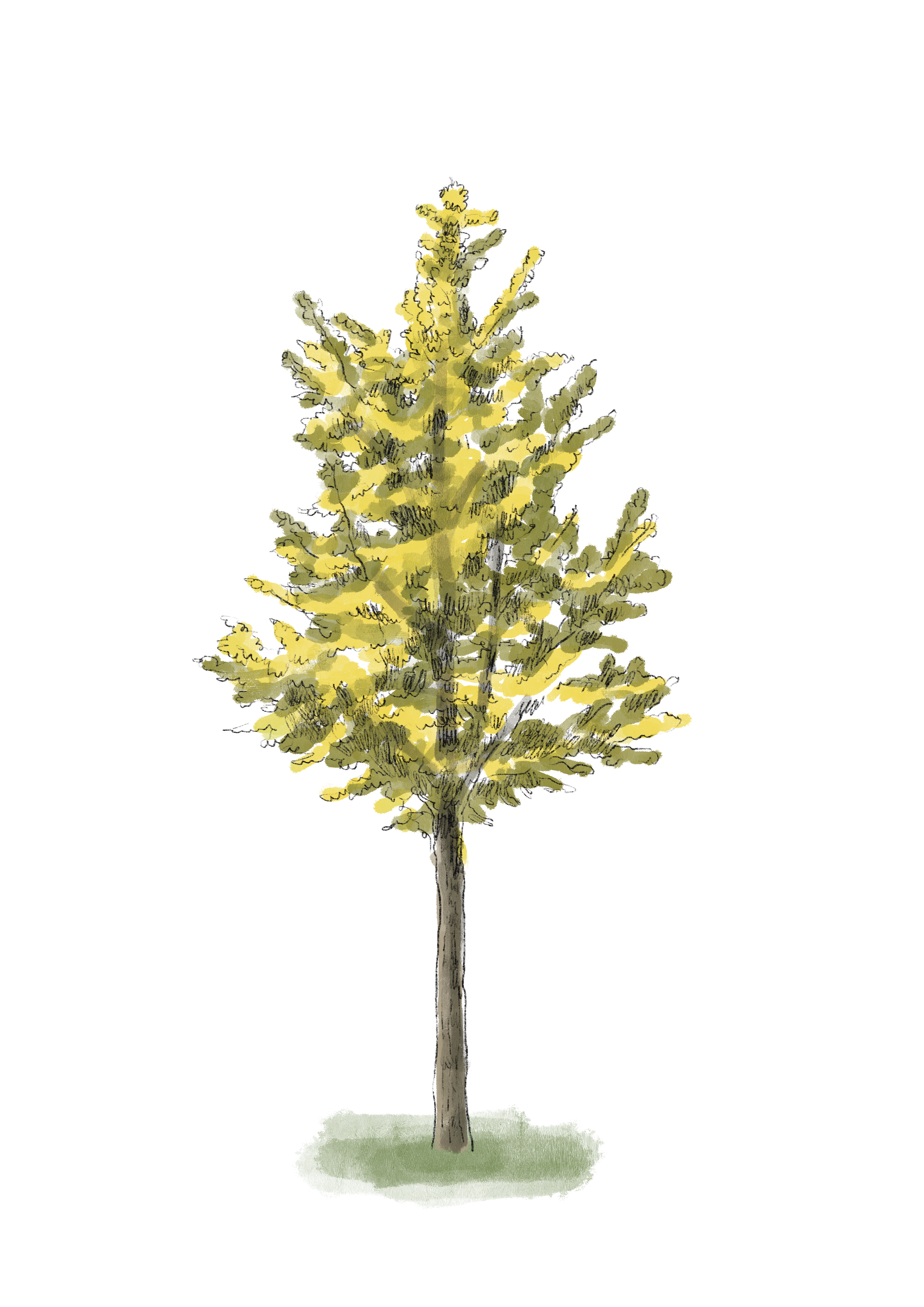
A deciduous tree with one or several elongated trunks. The leaves are fan-shaped, with radiating veins, light green in colour and darker on older trees; in autumn they become golden yellow. It is resistant to drought, wind, and snow, and its roots are deep. It can reach up to 30 m in height. The male and female flowers grow on separate trees, the male being the most used as the fruits from the female tree exude a very unpleasant foul-smelling aroma. They are slow-growing in the early years. It tolerates almost all types of soil, provided that they are well-drained, and prefers sunny locations. It spreads easily from seed.
Ginkgo biloba has been used by the Chinese for thousands of years for medicinal purposes, and in some religious ceremonies. The seeds are used as a “Yang” tonic for the kidneys, stimulating sexual energy and soothing bladder inflammation. The boiled seeds are also used as tea to treat lung problems (e.g. asthma) due to their anti-inflammatory and anti-allergenic action. The drupe is considered a delicacy, with aphrodisiac effects, used at weddings and parties; an overdose of the fruit can be quite toxic.
In the Western world, the most studied and used parts are the leaves; the relationship between Ginkgo extract and the cure or relief of Alzheimer’s has been studied, and it has been shown to improve cerebral blood supply and the performance of neurotransmitters; it improves circulatory problems (arteriosclerosis, blood circulation in the legs and feet, etc.), prevents decline in mental functions and regulates the heartbeat. It prevents the formation of free radicals responsible for the ageing of cells and has a strong neuro-protective action. Provides energy by increasing glucose uptake in cells. It inhibits platelet aggregation.
Ginkgo extract should not be taken with aspirin or warfarin as it increases the fluidity of the blood; it should not be taken by pregnant women. It should neither be taken in pre- or post-surgery periods because of the risk of haemorrhages. The seed shells when touched can cause dermatitis.
Ginkgo biloba is native to China, and was brought to Japan in the 19th century. and then to Holland; it is believed that there are trees in Japan which are about 3.000 years old. This is the only species of its kind and the only survivor of a group of trees that disappeared millions of years ago, and is therefore called a “living fossil”. Several wild specimens are known to exist in the mountains of Zhejiang (eastern China) when it was thought they no longer existed.
They are the ideal trees to plant in streets and public gardens as they are very resistant to storms, disease, and air pollution.
Ginkgo biloba is on the red list of plants threatened with extinction due to human action. Ginkgoes were among the few living creatures that survived the atomic bombing of Hiroshima, Japan. Several specimens were found ten kilometres from the site of the explosion.
Video
Video Botanical Trail
Município de Castanheira de Pera
Maidenhair Tree